 Linux OpenMP Benchmark Results
Linux OpenMP Benchmark Results
Contents
General
OpenMP is a system independent set of procedures and software that arranges automatic parallel processing of shared memory data when more than one processor is provided. This option is available in the C/C++ compiler included in the Linux Ubuntu Distribution.
In using OpenMP functions, I assumed that it would work in the same way as a vectorizing compiler as used on supercomputers. The most popular program used to demonstrate supercomputer performance is the Linpack Benchmark, the
scalar version
is included in this collection. Performance is governed by the following linked triad in a loop:
for(i=0; i < n; i++)
{
dy[i] = dy[i] + da * dx[i]
}
All that is required to parallelise the code is the following and a -fopenmp parameter in the compile command. Without this parameter, the program compiles normally, with the #pragma being ignored.
#pragma omp parallel for
for(i=0; i < n; i++)
{
dy[i] = dy[i] + da * dx[i]
}
The benchmark execution files and source code along with compile and run instructions can be downloaded in
linux_openmp.tar.gz.
Latest results are for a quad core/8 thread 3.7 GHz Core i7 4820K with 10 MB L3 cache, normally running at Turbo Burst speed of 3.9 GHz. It has 32 GB DDR3 RAM on 4 memory channels with maximum speed of 800 MHz (bus speed) x 2 (DDR) x 4 (channels) x 8 (bus width) or 51.2 GB/second. The benchmarks were recompiled via Ubuntu 14.04 via GCC 4.8.2 that can handle later Intel CPU instructions, including AVX1 and results are included below.
Further details of the AVX versions are in
Linux AVX benchmarks.htm.
The benchmarks and revised source codes are in
AVX_benchmarks.tar.gz.
To Start
MemSpeed
MemSpeed benchmark
employs three different sequences of operations, on 64 bit double precision floating point numbers, 32 bit single precision numbers and 32 bit integers via two data arrays:
Sum to register r = r + x [m] * y[m] (Integer + y [m])
Sum to memory x[m] = x[m] + y[m]
Memory to memory x[m] = y[m]
MemSpd2K, the latest standard version, uses assembly code to execute the same instructions as the original MemSpeed benchmark. This special version for OpenMP is again all C code, with the first linked triad tests returning results to memory via:
Sum to memory x[m] = x[m] + r * y[m]
Memory tested doubles up from 4 KB to 25% of RAM size, to use all caches and RAM. Speed measurements are data reading speeds in MegaBytes Per Second. For the linked triad tests, speed in MFLOPS can be calculated as MB/second divided by 4 for single precision floating point tests and divided by 8 for those using double precision.
Four MemSpeed execution files are provided with normal and OpenMP calculations compiled for 32-Bit and 64-Bit hardware -
memory_speed32, memory_speed32OMP, memory_speed64 and memory_speed64OMP.
Integer tests for the latter use 64 bit data words and SSE/SSE2 instructions are generated for floating point instead of the old x87 codes.
Note that the compiled code does not necessarily run SSE/SSE2 instructions efficiently. See
32-Bit and 64-Bit Differences,
but See later.
To Start
Example Log Files
Below are results produced from running on a Quad CPU Phenom processor using 64-Bit Ubuntu.
It can be seen that performance is influenced by cache sizes, in this case, 64 KB L1 cache and 512 KB L2 cache per CPU core and 6 MB shared L3 cache.
#####################################################
Assembler CPUID and RDTSC
CPU AuthenticAMD, Features Code 178BFBFF, Model Code 00100F42
AMD Phenom(tm) II X4 945 Processor
Measured - Minimum 3013 MHz, Maximum 3013 MHz
Linux Functions
get_nprocs() - CPUs 4, Configured CPUs 4
get_phys_pages() and size - RAM Size 7.81 GB, Page Size 4096 Bytes
uname() - Linux, roy-64Bit, 2.6.35-22-generic
#33-Ubuntu SMP Sun Sep 19 20:32:27 UTC 2010, x86_64
#####################################################
Normal Compilation
Memory Reading Speed Test 64 Bit Version 4 by Roy Longbottom
Start of test Tue Dec 7 09:40:17 2010
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+y[m] x[m]=y[m]
KBytes Dble Sngl Int64 Dble Sngl Int64 Dble Sngl Int64
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 21946 17235 35860 22906 18867 35859 22313 13661 18091
8 22605 17675 37302 23577 19332 37301 23305 13977 18738
16 22873 17868 37917 23834 19439 37916 23687 14150 18974
32 22998 17970 38233 23965 19526 38233 23892 14241 19124
64 23066 17978 38391 24029 19620 38390 23990 8021 19199
128 17491 15870 22707 17582 17096 22709 11432 7881 11307
256 17435 15738 22512 17313 16852 22512 11359 7968 11189
512 16530 15378 19598 16577 16264 19604 9923 9806 9856
1024 10120 10138 9962 10201 10196 9963 5000 4982 4974
2048 10145 10158 9970 10220 10215 9968 5004 4986 4974
4096 9859 9794 9751 9957 9939 9758 4887 4859 4879
8192 6593 6240 6769 6699 6577 6807 3459 3409 3449
16384 6310 6070 6430 6302 6280 6498 3209 3253 3265
32768 6378 6032 6484 6353 6341 6480 3267 3190 3265
65536 6340 6010 6462 6390 6287 6463 3252 3234 3246
131072 6350 6044 6484 6389 6308 6482 3257 3247 3289
262144 6390 6088 6478 6419 6323 6458 3224 3249 3304
524288 6403 6065 6475 6326 6374 6498 3224 3185 3275
1048576 6390 6032 6454 6457 6366 6373 3230 3212 3306
2097152 6376 6051 6465 6377 6329 6468 3239 3233 3279
End of test Tue Dec 7 09:40:58 2010
OPenMP Version
Memory Reading Speed Test 64 Bit Version 1 by Roy Longbottom
Start of test Sun Dec 5 12:26:36 2010
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+y[m] x[m]=y[m]
KBytes Dble Sngl Int64 Dble Sngl Int64 Dble Sngl Int64
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 2413 2340 2426 2408 2371 2593 1301 1302 1306
8 4642 4379 4655 4739 4488 5045 2562 2478 2583
16 8321 7942 8513 9215 8412 9668 4989 4695 4982
32 15714 12698 15446 16397 14036 17359 9112 7963 9159
64 25533 18268 24526 26971 21394 28979 16033 12269 16032
128 36147 23064 34023 40018 28460 42871 23255 16389 23172
256 45821 26908 42782 21679 34353 57114 31501 20370 31889
512 46924 28555 46191 55514 35557 54808 33583 22754 33376
1024 45478 28681 45098 48798 34662 47103 25081 22172 24993
2048 36642 26993 36187 36523 32366 36917 18354 17985 18388
4096 30960 24342 30259 32057 26483 32862 17172 15049 17153
8192 22963 20257 22754 23462 21376 23910 12203 11223 12176
16384 8927 8774 8888 8947 8803 8951 4469 4454 4487
32768 8938 8817 8875 8963 3681 8964 4494 4465 4488
65536 8956 8863 8910 8959 8849 8981 4500 4474 4502
131072 8979 8918 8951 8830 8808 9022 4513 4494 4517
262144 8784 8657 8706 8760 8826 8919 4436 4422 4433
524288 8774 8478 8789 8732 8643 8864 4374 3703 4435
1048576 8664 8559 8617 8689 8612 8678 4368 4360 4336
2097152 8661 8631 8643 8611 8597 8692 4364 4368 4367
End of test Sun Dec 5 12:27:13 2010
|
To Start
64 Bit, 32 Bit and Windows Comparisons, Phenom
Normal Compilation - Following are results on the above 3 GHz Phenom based system, for the first three tests at 64 bits and 32 bits using Ubuntu plus 32 bits via Windows 7 (see
OpenMP Speeds.htm).
Using Ubuntu and looking at floating point speeds in Millions of Floating Point Operations Per Second (MFLOPS), with 64 bit compilations, using SSE and SSE2, maximum double precision speed approaches one result per CPU clock cycle at 2883 MFLOPS but single precision comes out better at nearly 4500 MFLOPS. The maximum x87 speeds, at 32 bit working, are similar for both single and double precision at 2800 MFLOPS.
The integer code is not compiled as was expected (over optimised), but this does not matter in comparing. Both 64 bit and 32 bit versions are translated to eleven integer instructions per eight data words. Therefore, speed in Millions of Instructions Per Second (MIPS) is up to 6600 MIPS, at 64 bits, or 4000 MIPS at 32 bits.
The Windows based results are similar to those for Ubuntu, with data in L1 cache, but somewhat slower with data in L2 cache, L3 cache and RAM.
OpenMP Compilations - It was indeed a shock to see the pathetic slow speeds when using four CPUs, confirmed by performance monitor showing 100% utilisation on all. Analysis of results indicates that there is a startup delay involved, of around 1.7 microseconds in the case of the Ubuntu compilation/run. This is not as high as the
9 microseconds via Windows
but the latter appears to have a lower ongoing overhead. At 32 bits, maximum gains of the three measurements are 3.7, 2.3 and 2.0 times with Ubuntu then 4.6, 4.3 and 4.4 times with Windows. Greater than four times is possible when L3 cache sized data is shared amongst four L2 caches.
Below are results on from a PC with a 2.4 GHz Core 2 Duo processor. Here maximum gains on using both CPUs are up to 1.6 times using Windows but, other than with data in RAM, Ubuntu is often slower using both cores.
By using the gcc -S parameter to provide an assembly listing, it was found that the 64 bit compilation, when not requesting OpenMP, resulted in some full SIMD SSE instructions, whereby four multiplies or adds can be executed per clock cycle. This leads to the relative MP comparisons being less than they could be for both types of processor.
64 Bit Ubuntu 32 Bit Ubuntu 32 Bit Windows
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+
KBytes Dble Sngl Int Dble Sngl Int Dble Sngl Int
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 21946 17235 35860 21428 11040 11551 22924 11651 12725
8 22605 17675 37302 22078 11168 11555 23536 11839 13242
16 22873 17868 37917 22336 11231 11647 23834 11887 12790
32 22998 17970 38233 22460 11261 11684 23407 11902 13659
64 23066 17978 38391 22519 11275 11575 23669 11847 12910
128 17491 15870 22707 17075 9468 10026 14703 9926 10290
256 17435 15738 22512 16989 9431 9945 14644 9906 10175
512 16530 15378 19598 16597 9376 9847 14302 9921 10171
1024 10120 10138 9962 10092 8434 8270 8246 7091 7026
2048 10145 10158 9970 10109 8429 8269 8166 6976 7142
4096 9859 9794 9751 9855 8184 8045 8006 6898 6984
8192 6593 6240 6769 6531 5989 6267 4416 3983 4175
16384 6310 6070 6430 6274 5861 6148 4244 3888 3993
32768 6378 6032 6484 6180 5844 6119 4249 3885 3958
65536 6340 6010 6462 6169 5803 6095 4235 3892 3929
131072 6350 6044 6484 6112 5840 6124 4264 3894 3965
262144 6390 6088 6478 6158 5840 6104 4279 3870 3991
524288 6403 6065 6475 6085 5817 5980 4235 3873 3968
OpenMP Using 4 CPUs
4 2413 2340 2426 2387 2108 2060 418 436 439
8 4642 4379 4655 4469 3872 3698 874 862 866
16 8321 7942 8513 8194 6297 6122 1727 1713 1700
32 15714 12698 15446 13347 8921 8657 3341 3234 3263
64 25533 18268 24526 18662 11155 10740 6123 5792 5978
128 36147 23064 34023 23357 12784 12286 10822 9932 10085
256 45821 26908 42782 27111 13916 13245 17639 15485 16134
512 46924 28555 46191 27574 14148 13196 25742 22009 22123
1024 45478 28681 45098 28696 14428 13452 33657 27622 26572
2048 36642 26993 36187 29056 14493 5942 37554 30171 31756
4096 30960 24342 30259 26326 14192 12892 24280 22284 23117
8192 22963 20257 22754 23863 13865 12563 16476 13555 15907
16384 8927 8774 8888 8777 8709 8658 7394 7137 7077
32768 8938 8817 8875 8887 8700 8679 7387 6969 7184
65536 8956 8863 8910 8915 8716 8701 7486 7188 7240
131072 8979 8918 8951 8931 8719 8735 7462 7163 7249
262144 8784 8657 8706 8866 8591 8294 7578 7207 7280
524288 8774 8478 8789 8710 8197 8264 7652 7405 7344
|
To Start
Core 2 Duo Results
64 Bit Ubuntu 32 Bit Ubuntu 32 Bit Windows
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+
KBytes Dble Sngl Int Dble Sngl Int Dble Sngl Int
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 17307 12410 18880 17333 8611 9470 18490 9185 9190
8 17230 12597 18835 17224 8698 9536 18631 9349 9490
16 17395 12701 19021 17396 8737 9569 18903 9467 9367
32 17481 12755 19104 17471 8751 9571 18739 9487 9440
64 11757 11813 12069 11731 7632 7993 11535 7631 7874
128 11769 11826 12099 11735 7629 7991 11626 7584 7890
256 11773 11834 12106 11747 7635 7997 11634 7686 7868
512 11777 11838 12109 11749 7638 8000 11632 7524 7897
1024 11779 11835 12111 11745 7617 7996 11605 7638 7929
2048 11663 11666 11998 11668 7530 7908 11408 7298 7743
4096 9505 9534 9724 8895 6843 7149 8626 7057 7242
8192 4496 4502 4449 4580 4580 4594 4287 4222 4305
16384 3922 3903 3884 4036 4052 4041 3690 3532 3678
32768 3888 3868 3847 3926 3902 3943 3284 3431 3539
65536 3894 3877 3852 3933 3938 3950 3572 3460 3550
131072 3851 3837 3805 3897 3898 3907 3485 3550 3528
262144 3867 3847 3823 3911 3912 3922 3504 3570 3400
524288 3879 3856 3829 3906 3908 3919 3650 3533 3440
OpenMP Using 2 CPUs
4 3753 3188 3728 2423 1953 1908 425 413 440
8 6063 4722 5937 4074 2903 2751 842 830 821
16 8992 6258 8678 6024 3758 3586 1681 1630 1607
32 11799 7391 11120 7942 4372 4204 2558 2640 2908
64 13713 8112 12689 8960 4773 4512 5148 4751 4700
128 15128 8636 13996 9975 4890 4622 7553 6765 6987
256 16109 8881 14739 10557 5028 4752 10645 8937 8613
512 16560 9034 15156 10837 5130 4820 12273 10469 11132
1024 16790 9101 15353 11024 5140 4844 13733 9631 11788
2048 16682 9092 15310 11057 5166 4856 15255 11028 12647
4096 8333 7509 8566 9226 5065 4781 13525 10211 11712
8192 4513 4560 4590 4722 4445 4306 4367 4318 3582
16384 4106 4081 4110 4103 4045 4016 3409 3718 3706
32768 3960 3951 3966 4077 4043 3998 2815 3017 3575
65536 3961 3956 3948 4105 4071 4055 3570 3602 3401
131072 3991 3996 3983 4027 4025 4011 3656 3466 3614
262144 3992 4016 3988 4066 4084 4034 3727 3564 3720
524288 4036 4018 4017 3939 4042 4030 3737 3637 3641
|
To Start
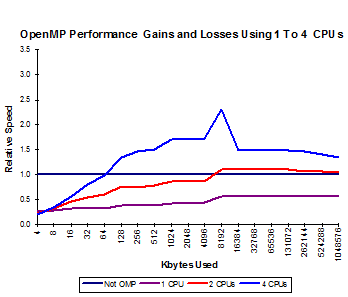
Results Using 1 to 4 CPUs
The OpenMP execution codes can be run with a parameter than dictates which CPU or CPUs are used, as with Windows Affinity options. With Ubuntu an example to run on the first CPU is:
taskset 0x00000001 ./memory_speed64OMP
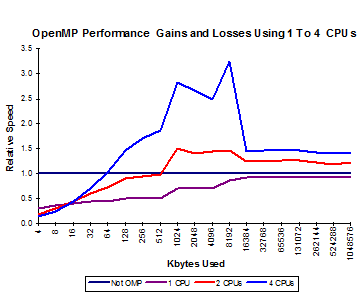
Then it is 0x00000003 for the first two cores and 0x00000007 for three. Anyway, the graphs below show performance gains and losses of the 32 bit and 64 bit OpenMP compilations using single precision floating point variables.
32 Bit Single Precision Floating Point x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m]
|
|
64 Bit Single Precision Floating Point x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m]
|
To Start
Original OpenMP Benchmark
My first OpenMP performance tests executed the same instruction sequences as used in a
CUDA Benchmark.
The arithmetic operations executed are of the form x[i] = (x[i] + a) * b - (x[i] + c) * d + (x[i] + e) * f with 2, 8 or 32 operations per input data word. Array sizes used are 0.1, 1 or 10 million 4 byte single precision floating point words.
The program checks for consistent numeric results, primarily to show that all calculations are carries out. These are quite sensitive, where a change of 1 of Repeat Passes changes 0.929475 to 0.929448. However, SSE and x87 calculations produce slightly
different answers.
Four execution files are again provided with normal and OpenMP calculations compiled for 32-Bit and 64-Bit hardware - openMPmflops32, openMPmflops64, notOMPmflops32 and notOMPmflops364. Below is an example of results on the 3 GHz Quad Core Phenom, showing maximum speed of nearly 15 GFLOPS.
32 Bit OpenMP MFLOPS Benchmark 1 Thu Dec 9 16:48:08 2010
Via Ubuntu 32 Bit Compiler
Test 4 Byte Ops/ Repeat Seconds MFLOPS First All
Words Word Passes Results Same
Data in & out 100000 2 2500 0.086841 5758 0.929475 Yes
Data in & out 1000000 2 250 0.074519 6710 0.992543 Yes
Data in & out 10000000 2 25 0.163307 3062 0.999249 Yes
Data in & out 100000 8 2500 0.149781 13353 0.957164 Yes
Data in & out 1000000 8 250 0.147888 13524 0.995525 Yes
Data in & out 10000000 8 25 0.176824 11311 0.999550 Yes
Data in & out 100000 32 2500 0.537051 14896 0.890377 Yes
Data in & out 1000000 32 250 0.534446 14969 0.988102 Yes
Data in & out 10000000 32 25 0.537515 14883 0.998799 Yes
|
To Start
OpenMPMFLOPS comparisons
Following are MFLOPS of normal compilations for a single CPU compared with OpenMP speeds for all processors, on a quad core Phenom and Core 2 Duo, at 32 bits and 64 bits. The 32 bit versions, using x87 instructions, behave in the same way as the
Windows version,
where quad core OpenMP throughput is up to nearly four times faster than the normal single CPU speeds. This is not the case at 64 bit working, using SSE instructions, where dual core OpenMP speeds can be much slower than the single CPU normal compilation, and four cores are required to obtain the same performance.
The second set of results show OpenMP speeds using 1, 2, 3 and 4 cores on the Phenom (using the taskset execution parameter - see above). Here, performance can be nearly proportional to the number of cores requested.
See below for an explanation why 64 bit normal compilation produces much higher speeds using one CPU.
3 GHz Phenom 2.4 GHz Core 2 Duo
32 Bits 64 Bits 32 Bits 64 Bits
Data Ops/ 1 CPU 4 CPUs 1 CPU 4 CPUs 1 CPU 2 CPUs 1 CPU 2 CPUs
Words Word i387 OMP SSE OMP i387 OMP SSE OMP
100000 2 2439 5758 7624 5769 1602 2815 5556 2904
1000000 2 2231 6710 4686 6674 1590 2280 4292 2780
10000000 2 1739 3062 2195 2944 1173 1233 1251 1258
100000 8 3348 13353 14357 12126 3142 4665 13061 5212
1000000 8 3195 13524 13376 12420 3129 4878 11591 5152
10000000 8 3080 11311 7473 10976 3067 4430 4997 4861
100000 32 3881 14896 15336 13494 3316 5922 14486 6421
1000000 32 3853 14969 15009 13540 3341 5932 14320 6411
10000000 32 3817 14883 14318 13450 3334 5842 13750 6396
3 GHz Phenom 3 GHz Phenom
32 Bits i387 64 Bits i387
Data Ops/ 1 CPU 2 CPUs 3 CPUs 4 CPUs 1 CPU 2 CPUs 3 CPUs 4 CPUs
Words Word OMP OMP OMP OMP OMP OMP OMP OMP
100000 2 1903 3575 4678 5758 1974 3597 4770 5769
1000000 2 1787 3588 5300 6710 1913 3843 5564 6674
10000000 2 1509 2490 2832 3062 1590 2566 2867 2944
100000 8 3518 6963 10342 13353 3437 6835 10100 12126
1000000 8 3453 6943 10367 13524 3375 6802 10121 12420
10000000 8 3308 6541 9522 11311 3219 6379 9395 10976
100000 32 3794 7566 11310 14896 3552 7084 10601 13494
1000000 32 3774 7554 11317 14969 3533 7079 10616 13540
10000000 32 3735 7465 11166 14883 3490 6970 10440 13450
|
To Start
Netbook Hyperthreading MFLOPS
|
The 32 bit and 64 bit benchmarks were also run on a Netbook, having a 1.66 GHz Intel Atom N455 processor, both running via the 64 bit version of Ubuntu. This has a single core but includes Hyperthreading, where two processors are identified as available.
Floating point MFLOPS speed of the Atom is not very good compared with CPU MHz, but Hyperthreading can nearly double the speed. The processor supports SSE instructions, again not as efficiently as desktop CPUs, but this leads to best performance from the single thread 64 bit benchmark.
Below are one and two thread MemSpeed OpenMP speeds, converted to MFLOPS, plus those without using OpenMP.
Single precision L1 cache results can be broadly compared with OpenMP FLOPS at two operations per word.
|
64 Bit 32 Bit
Data OMP OMP SSE OMP OMP i387
Words 1CPU 2CPU 1CPU 1CPU 2CPU 1CPU
2 Ops/Wd
100000 232 386 784 203 340 203
1000000 227 383 657 201 339 201
10000000 228 391 662 201 352 202
8 Ops/Wd
100000 505 892 1811 294 547 303
1000000 500 883 1736 293 547 302
10000000 498 900 1745 294 552 302
32 Ops/Wd
100000 506 963 1832 403 783 404
1000000 505 965 1817 403 762 404
10000000 506 971 1819 403 784 403
|
|
The only areas where OpenMP provides the best performance, at 64 bits, are double precision calculations from data in L2 Cache and RAM, then the same at single and double precision with 32 bit compilation.
|
64 Bit MFLOPS 32 Bit MFLOPS
OMP OMP OMP OMP SSE2 SSE OMP OMP OMP OMP SSE2 SSE
1CPU 1CPU 2CPU 2CPU 1CPU 1CPU 1CPU 1CPU 2CPU 2CPU 1CPU 1CPU
Dble Sngl Dble Sngl Dble Sngl Dble Sngl Dble Sngl Dble Sngl
L1 Cache 106 150 114 235 262 745 108 157 89 165 243 246
137 181 225 330 265 748 151 187 162 231 246 246
L2 Cache 182 223 364 464 226 604 186 212 287 323 213 228
171 214 379 468 226 606 187 206 296 330 213 228
RAM 175 220 248 445 208 515 175 204 246 327 192 215
175 221 254 445 208 513 176 205 247 328 196 217
|
To Start
MemSpeed Core i7
Below are 64 bit MemSpeed compilations using AVX instructions and default with SSE type, then both compiled to use OpenMP (4 cores, 8 threads).
Using AVX1 instructions, maximum double precision speed is 3.9 GHz x 4 (register width) x 2 (multiply and add) = 31.2 GFLOPS. These instructions are used for MemSpeed, without OpenMP compiling directives - see Assembly Code.
Maximum DP speed was 7.9 GFLOPS, restricted due to overheads of loading, storing and inserting data. These also limited performance gains, compared with SSE types.
For both SSE and AVX OpenMP compilations, SISD instructions were generated, leading to no difference in speed (one number at a time out of 2 or 4 DP, and 4 or 8 SP). Shared L3 cache sized data was required for real MP performance gains, with startup and cache flushing overheads limiting speed using other caches.
As indicated earlier, maximum memory transfer speed is 51.2 GB/second. It appears that multiple CPUs are needed for maximum throughput, and the up to 25 GB/second obtained via OpenMP is quite respectable.
CPU GenuineIntel, Features Code BFEBFBFF, Model Code 000306E4
Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4820K CPU @ 3.7 GHz at 3.9 GHz Turbo Boost
Memory Reading Speed Test 64 Bit Version 4.1 by Roy Longbottom
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+y[m] x[m]=y[m]
KBytes Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 39311 24057 52483 40345 24058 52352 28687 15957 29066 L1
8 39076 24566 57022 40079 24470 57001 30005 15794 30071
16 39851 24795 59688 40773 24768 59685 30605 15683 30691
32 39859 24862 60824 41216 24876 61083 28148 15675 30978
64 32844 24462 47825 34369 24707 47838 23819 15646 29441 L2
128 32879 24498 48223 34308 24841 48325 23978 15603 29659
256 30516 23886 43374 31823 24290 43355 20623 15412 26554
512 25604 22420 30617 26141 22961 30617 15299 13893 17247 L3
1024 25565 22368 30352 26103 22992 30275 15124 13823 17145
2048 25589 22479 30344 26056 23017 30339 15120 13793 17155
4096 25600 22405 30332 26136 23025 30249 15122 13829 17159
8192 25593 22460 30297 26025 22997 30299 15110 13832 17160
16384 15083 14415 14745 15085 14690 14752 7484 7601 7464 RAM
32768 14845 14293 14391 14840 14313 14382 7331 7480 7330
65536 14959 14424 14498 14961 14466 14490 7387 7518 7343
131072 15041 14492 14607 15048 14592 14608 7416 7550 7371
262144 15023 14491 14598 15017 14595 14601 7406 7523 7377
524288 15053 14520 14645 15096 14666 14659 7424 7570 7395
1048576 15085 14534 14659 15093 14675 14650 7432 7565 7396
2097152 15096 14538 14670 15109 14687 14649 7433 7573 7401
4194304 15096 14544 14665 15108 14684 14673 7434 7570 7402
Max GFLOPS 5.0 6.2
Memory Reading Speed Test 64 Bit AVX v4.1 by Roy Longbottom
Start of test Fri Dec 5 11:00:23 2014
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+y[m] x[m]=y[m]
KBytes Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 60540 56699 52591 57703 56568 57922 37596 37416 37400 L1
8 61747 57965 57139 60342 60007 60148 39695 39314 39280
16 62152 59667 59718 61363 61268 61332 40675 40425 40426
32 62236 59589 61081 61973 61907 61923 40453 40503 40172
64 48504 42393 48777 49339 49179 48854 30898 30520 30369 L2
128 47554 41906 47884 48347 48245 47791 29682 29561 29698
256 39989 36923 40809 41397 41077 40806 26011 25996 25973
512 30999 30198 31130 31333 31336 31130 17511 17498 17504 L3
1024 30115 29285 30356 30676 30669 30356 17155 17153 17151
2048 30093 29338 30337 30667 30641 30339 17175 17173 17171
4096 30083 29362 30301 30654 30650 30313 17183 17186 17185
8192 29826 29119 30051 30381 30371 30055 17015 17005 16977
16384 15242 15364 15114 15083 15089 15133 7543 7538 7527 RAM
32768 14709 14860 14612 14551 14547 14624 7313 7309 7306
65536 14807 14959 14656 14590 14594 14656 7361 7352 7350
131072 14857 15026 14654 14612 14621 14666 7392 7381 7377
262144 14860 15018 14644 14612 14625 14652 7392 7373 7382
524288 14865 15044 14674 14635 14657 14651 7394 7391 7382
1048576 14880 15041 14692 14634 14649 14674 7402 7391 7392
2097152 14883 15048 14685 14640 14655 14685 7401 7394 7389
4194304 14884 15050 14704 14643 14642 14686 7403 7393 7395
Max GFLOPS 7.9 15.1
AVX Average Performance Gain
L1 1.56 2.38 1.00 1.49 2.44 1.05 1.35 2.50 1.30
L2 1.41 1.66 0.98 1.38 1.87 0.98 1.27 1.84 1.00
L3 1.18 1.31 1.00 1.18 1.34 1.00 1.14 1.24 1.00
RAM 0.99 1.04 1.01 0.97 1.00 1.01 1.00 0.98 1.00
Memory Reading Speed Test 64 Bit OPenMP v4.1 by Roy Longbottom
Start of test Fri Nov 28 17:55:17 2014
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+y[m] x[m]=y[m]
KBytes Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 2666 2628 2637 2666 2648 2656 1336 1340 1341 L1
8 5058 4962 5001 5184 5038 5005 2665 2604 2609
16 9662 9412 9612 10322 9790 9637 5234 5045 5060
32 18780 17122 18026 19562 18224 18349 9934 9414 9490
64 33953 26599 27774 36787 32353 32596 18894 16772 17154 L2
128 51235 36875 36401 58443 44166 44785 31628 24488 24758
256 70872 47353 45667 82647 58676 57787 46448 32315 32563
512 90020 53395 51148 106043 68693 66363 61909 39171 39181 L3
1024 97333 57510 53608 115688 73680 71162 69650 41461 41234
2048 96621 58092 56214 105074 75938 74497 57895 43166 42881
4096 87122 60230 57450 108329 79312 76890 60543 44350 44679
8192 94138 60267 57038 111782 80836 78310 61701 45373 45276
16384 27817 27128 27652 28042 27209 27621 14155 14067 14081 RAM
32768 24666 24563 24251 24689 24525 24623 12491 12431 12437
65536 24868 25137 24941 24889 25022 25066 12683 12623 12598
131072 25625 25696 25301 25566 25606 25593 12904 12729 12793
262144 25603 25435 25446 25482 25534 25410 12908 12788 12782
524288 25603 25634 25381 25560 25575 25534 12915 12847 12835
1048576 25569 25690 25662 25572 25516 25427 12910 12803 12881
2097152 25634 25814 25625 25581 25601 25648 12886 12846 12875
4194304 25344 25266 25151 25459 24722 25457 12780 12686 12749
Max GFLOPS 12.1 14.9
Memory Reading Speed Test 64 Bit AVX OMP v4.1 by Roy Longbottom
Start of test Fri Dec 5 11:09:53 2014
Memory x[m]=x[m]+s*y[m] Int+ x[m]=x[m]+y[m] x[m]=y[m]
KBytes Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32 Dble Sngl Int32
Used MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S MB/S
4 2683 2592 2563 2686 2594 2625 1333 1333 1332 L1
8 4584 4964 5000 5239 5083 5057 2647 2622 2626
16 9056 9413 9449 10368 9793 9667 5236 5068 5068
32 19081 17114 17137 19631 18253 18260 10037 9452 9455
64 33828 26953 27654 36957 31205 31589 18841 16782 17235 L2
128 51222 34104 37139 59422 45145 46240 31286 24311 24595
256 65935 47007 45285 84331 58294 56615 46805 32592 32531
512 90277 53407 51487 106561 69159 66613 62416 39263 38593 L3
1024 97954 57535 53920 116050 73787 71152 69141 42793 42486
2048 73879 57775 56074 106129 76487 75147 59042 43105 42679
4096 100558 59738 57252 108882 79594 77143 61164 44567 44514
8192 104058 58948 57444 109523 79733 76361 59637 44882 44819
16384 27756 27436 27917 27988 27893 27965 14311 14043 14223 RAM
32768 24601 24109 24243 24588 24408 24464 12395 12293 12169
65536 25198 25230 24848 25202 25191 25191 12691 12632 12587
131072 25621 25685 25370 25679 25604 25682 12956 12874 12859
262144 25815 25798 25749 25767 25766 25521 12906 12888 12880
524288 25910 25884 25686 25741 25778 25780 12953 12945 12870
1048576 26016 26010 25889 25859 25896 25761 12943 12894 12948
2097152 25898 25948 25708 25784 25727 25855 13000 12929 12899
4194304 25730 25660 25617 25600 25698 25690 12815 12782 12877
Max GFLOPS 12.6 14.9
Comparison OpenMP AVX/Not AVX - Average
L1 0.97 1.00 0.98 1.01 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
L2 0.98 0.98 1.00 1.01 0.99 0.99 1.00 1.00 1.00
L3 1.01 0.99 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.01 1.00
RAM 1.01 1.01 1.01 1.01 1.01 1.01 1.00 1.00 1.00
Comparison AVX OPenMP/Not OpenMP - Average
L1 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.12 0.12 0.12
L2 1.14 0.91 0.82 1.34 1.00 1.00 1.15 0.88 0.88
L3 3.09 1.95 1.82 3.56 2.47 2.41 3.62 2.50 2.48
RAM 1.72 1.70 1.73 1.75 1.74 1.74 1.74 1.73 1.73
|
To Start
OpenMP MFLOPS Core i7
The first results below are from 64 bit SSE compilations without OpenMP directives, testing one core, where up to 24.4 GFLOPS, out of a maximum of 31.2, is quite respectable. The same program code was run with Pthread functions, where the number of threads to use is an input parameter. Details can be found in
Linux Multithreading Benchmarks.htm.
Using 8 threads via 4 cores, this produced up to 93.2 GFLOPS with SSE and 177.8 using AVX.
The version, compiled with OpenMP directives, was run using an affinity setting to use one CPU core, besides the default that uses all cores. At least the MP runs provided performance gains approaching four times, but speeds were slow, compared with non-OpenMP tests. At 2 and 8 operations per word, full SIMD instructions demonstrated suitable AVX performance improvements, but relatively slow, due to data handling overheads, as MemSpeed. With 32 operations per word, SISD instructions were generated, again, leading to the same SSE and AVX speeds.
Note that the SSE OpenMP speeds shown below are from a recompiled version by GCC 4.8.2, as this produces SIMD instructions. The new versions are included in
AVX_benchmarks.tar.gz.
The original version, in
linux_openmp.tar.gz,
uses SISD instructions with maximum speeds of 6.1 GFLOPS, using 1 core, and 23.2 GFLOPS flat out, the latter being the same as the new version at 32 operations per word.
--------------- OpenMP --------------
4 Byte Ops/ Repeat SSE ------ SSE ------ ------ AVX ------
Words Word Passes 1 Core affinity1 4 Cores affinity1 4 Cores
100000 2 2500 9918 6061 13742 10196 19577
1000000 2 250 9688 6215 19477 10025 37906
10000000 2 25 5870 5059 9137 5880 7782
100000 8 2500 24448 13220 44104 26481 88370
1000000 8 250 24465 13373 49499 27045 90579
10000000 8 25 20055 12719 38369 20593 35607
100000 32 2500 23251 5854 22858 5865 22845
1000000 32 250 23265 5863 23234 5870 23141
10000000 32 25 23063 5860 23127 5854 23077
|
To Start
Assembly Code
Below are disassemblies of the loops using 32 operations per data word, compiled for 64 bit working, where SSE instructions are produced. The normal compilation uses full SIMD instructions where four adds, subtractions or multiplies (addps, subps or mulps) are executed at the same time, and the loop increment is 4 words or 16 bytes (addq $16). The OpenMP code produces uses Single Instruction Single Data (SISD) functions (addss, subss or mulss) with a loop increment of 1 word (addq $4). The SISD sequence is also included along with the SIMD code, for the last 1 to 3 words, if required.
A 32 bit non-OpenMP version, compiled to use SSE instructions, was also produced (gcc -msse parameter). This also employed SIMD and generated the same high levels of performance as the 64 bit normal variety.
64 Bit Normal Compilation 64 Bit OpenMP Compilation
.L7: .L14:
movaps (%r8,%rdx), %xmm1 movss (%rdx), %xmm1
addl $1, %ecx addl $1, %ecx
movaps %xmm1, %xmm0 movss 12(%rbx), %xmm0
movaps %xmm1, %xmm2 movss 20(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm15, %xmm0 addss %xmm1, %xmm0
addps %xmm13, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps %xmm14, %xmm0 mulss 16(%rbx), %xmm0
mulps %xmm12, %xmm2 mulss 24(%rbx), %xmm2
subps %xmm2, %xmm0 subss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps %xmm1, %xmm2 movss 28(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm11, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps %xmm10, %xmm2 mulss 32(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm2, %xmm0 addss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps %xmm1, %xmm2 movss 36(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm9, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps %xmm8, %xmm2 mulss 40(%rbx), %xmm2
subps %xmm2, %xmm0 subss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps %xmm1, %xmm2 movss 44(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm7, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps %xmm6, %xmm2 mulss 48(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm2, %xmm0 addss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps %xmm1, %xmm2 movss 52(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm5, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps %xmm4, %xmm2 mulss 56(%rbx), %xmm2
subps %xmm2, %xmm0 subss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps %xmm1, %xmm2 movss 60(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm3, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps 40(%rsp), %xmm2 mulss 64(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm2, %xmm0 addss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps 24(%rsp), %xmm2 movss 68(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm1, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps 8(%rsp), %xmm2 mulss 72(%rbx), %xmm2
subps %xmm2, %xmm0 subss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps -8(%rsp), %xmm2 movss 76(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm1, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
mulps -24(%rsp), %xmm2 mulss 80(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm2, %xmm0 addss %xmm2, %xmm0
movaps -40(%rsp), %xmm2 movss 84(%rbx), %xmm2
addps %xmm1, %xmm2 addss %xmm1, %xmm2
addps -72(%rsp), %xmm1 addss 92(%rbx), %xmm1
mulps -56(%rsp), %xmm2 mulss 88(%rbx), %xmm2
mulps -88(%rsp), %xmm1 mulss 96(%rbx), %xmm1
subps %xmm2, %xmm0 subss %xmm2, %xmm0
addps %xmm1, %xmm0 addss %xmm1, %xmm0
movaps %xmm0, (%r8,%rdx) movss %xmm0, (%rdx)
addq $16, %rdx addq $4, %rdx
cmpl %r9d, %ecx cmpl %ecx, %eax
jb .L7 jg .L14
MemSpeed
AVX SIMD DP 4 multiplies, 4 adds AVX OpenMP SISD single adds
and multiples
vmovupd (%rsi,%rax), %xmm0 vaddsd -8(%rcx), %xmm0, %xmm0
vinsertf128 $0x1, 16(%rsi,%rax), %ymm0, %ymm0 vmovsd %xmm0, -8(%rcx)
vmovupd (%rdx,%rax), %xmm1 vmovsd (%rsi), %xmm0
vinsertf128 $0x1, 16(%rdx,%rax), %ymm1, %ymm1 vmulsd (%rbx), %xmm0, %xmm0
vmulpd %ymm2, %ymm0, %ymm0 vaddsd (%rcx), %xmm0, %xmm0
vaddpd %ymm0, %ymm1, %ymm0 vmovsd %xmm0, (%rcx)
vmovupd %xmm0, (%rdx,%rax) vmovsd 8(%rsi), %xmm0
vextractf128 $0x1, %ymm0, 16(%rdx,%rax vmulsd (%rbx), %xmm0, %xmm0
addq $32, %rax vaddsd 8(%rcx), %xmm0, %xmm0
|
To Start
 Roy Longbottom December 2014
Roy Longbottom December 2014
The Internet Home for my PC Benchmarks is via the link
Roy Longbottom's PC Benchmark Collection
|


 Roy Longbottom December 2014
Roy Longbottom December 2014